Effective Strategies for Grain Weevil Control
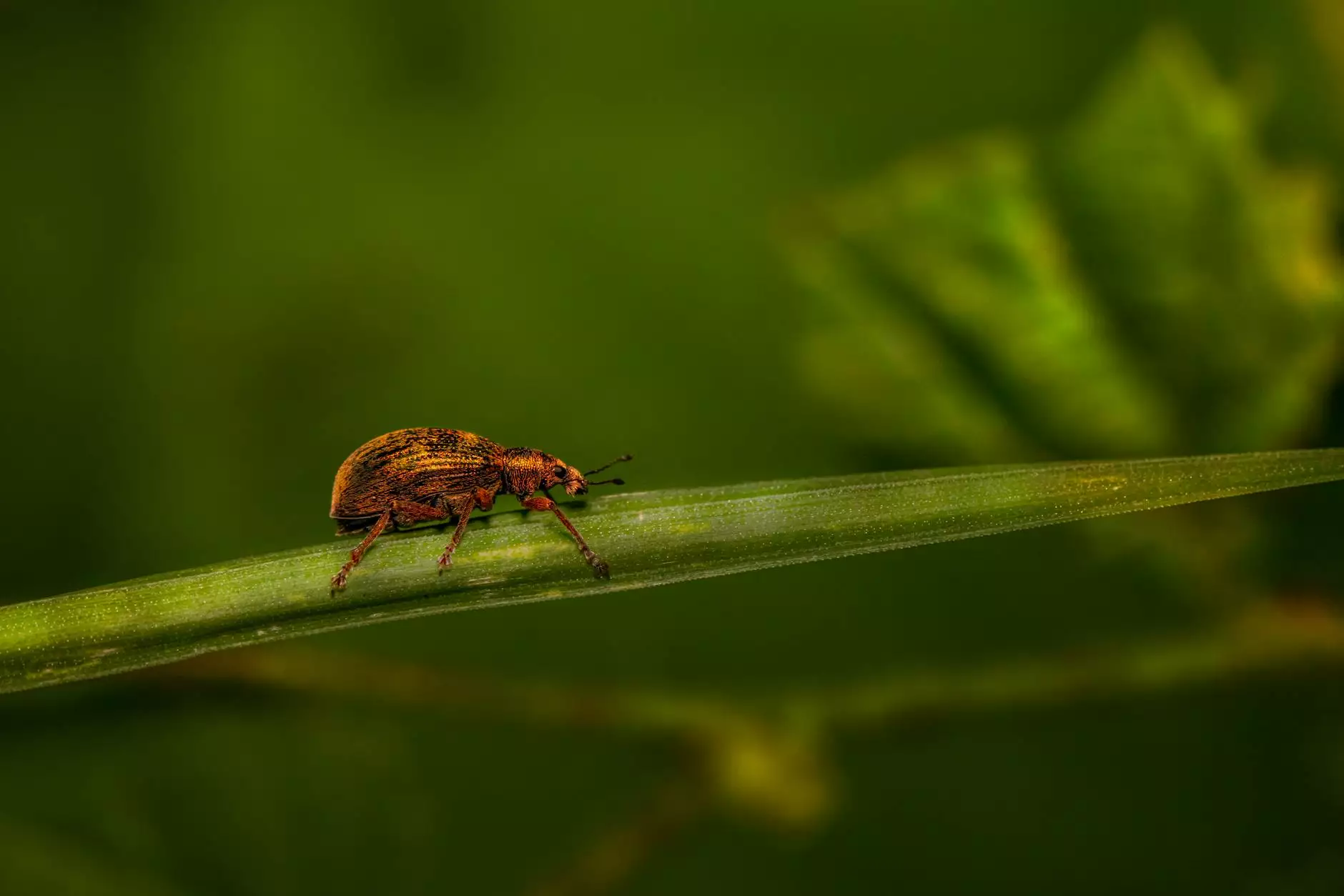

The presence of grain weevils in agricultural settings can create significant challenges for farmers and grain producers. These pests, particularly the Callosobruchus maculatus (the common bean weevil) and the Sitophilus granarius (the granary weevil), are notorious for infesting stored grains, leading to diminished crop value and quality. In this comprehensive guide, we will explore various aspects of grain weevil control, providing farmers with the knowledge necessary to safeguard their investments.
Understanding Grain Weevils
Before delving into control measures, it's essential to understand the biology and behavior of grain weevils. These pests are small (approximately 2.5 to 5 mm in length) and can be identified by their elongated snouts and distinct body shapes. They pose a significant threat to a variety of stored grains, such as:
- Wheat
- Rice
- Corn
- Barley
- Beans
Grain weevils feed on the interior of grains, laying their eggs inside the kernels. This can lead to severe losses in both quality and weight, making effective grain weevil control imperative for any operation involved in grain production.
Signs of Infestation
Identifying an infestation early is key to effective grain weevil control. Here are some common signs that can help farmers detect a weevil problem:
- Visible Adult Weevils: Spotting living adult weevils in or around storage areas is one of the first signs of infestation.
- Damaged Grain: Look for holes in grains, indicating the entry and exit points of weevils.
- Powdery Residue: Fine powder or frass, a byproduct of feeding, is often found in contaminated grain.
- Webbing and Cocoon Presence: Webbing may be present if larvae are part of the infestation.
Prevention Tactics for Grain Weevil Control
The most effective method of grain weevil control starts before an infestation occurs. Prevention requires a holistic approach that includes:
1. Proper Grain Storage
Storage conditions play a pivotal role in pest management. Implement the following storage practices:
- Use Sealed Containers: Ensure all grains are stored in airtight containers to reduce access for weevils.
- Maintain Low Moisture Content: Store grains at moisture levels below 12% to prevent weevil reproduction.
- Regular Cleaning: Clean storage areas regularly to eliminate any residual grains that could harbor pests.
2. Monitoring and Inspection
Routine monitoring and inspection of stored grains are vital for early detection. Employ tools and methods such as:
- Visual Inspections: Regularly check for signs of pests or damage.
- Sampling: Randomly sample grains to look for visible weevils and frass.
- Pheromone Traps: Use traps to catch weevils and monitor populations.
Control Methods for Existing Infestations
If an infestation has already occurred, it’s crucial to implement effective control methods. Here are several strategies that can help:
1. Physical Controls
These methods involve physical means to eliminate pests.
- Heat Treatment: Temperatures above 50°C (122°F) for several hours can eliminate weevils at all life stages.
- Cold Treatment: Conversely, freezing infested grains at -18°C (0°F) for at least four days can also be effective.
- Vacuuming: Regularly vacuuming storage areas can help remove adult weevils and debris.
2. Chemical Controls
In cases where physical controls may not suffice, chemical treatments can be utilized. Always follow safety protocols and local regulations:
- Insecticides: Select appropriate insecticides specifically labeled for grain weevil control and follow application guidelines.
- Grain Protectants: Using protectants during storage can provide a barrier against infestations.
3. Biological Controls
These involve the use of natural predators or biological agents to control pest populations effectively:
- Predatory Insects: Introducing natural enemies such as certain beetles can help reduce weevil populations.
- Microbial Insecticides: Bacteria and nematodes can also be used to target specific pests.
Best Practices for Grain Weevil Control
To effectively manage weevil populations and protect your grain investment, consider adopting the following best practices:
- Integrated Pest Management (IPM): A holistic approach combining physical, chemical, and biological methods ensures effective control.
- Training Staff: Educate employees on identification and management of grain pests.
- Record Keeping: Maintain records of pest sightings and treatment methods for future reference.
- Community Collaboration: Work with neighboring farms to monitor and manage pest control efforts collectively.
Conclusion
Effective grain weevil control is vital for farmers looking to protect their agricultural investments and maintain crop quality. By understanding the biology of these pests, implementing robust prevention strategies, and employing effective treatment methods, farmers can substantially reduce the risk of infestations. It is essential to regularly assess and adapt pest management strategies to suit specific farm operations. As a pivotal resource for agricultural insights, TSGC Inc. is here to support farmers with expert advice and exceptional service in farm equipment repair and farming equipment.